I. Introduction
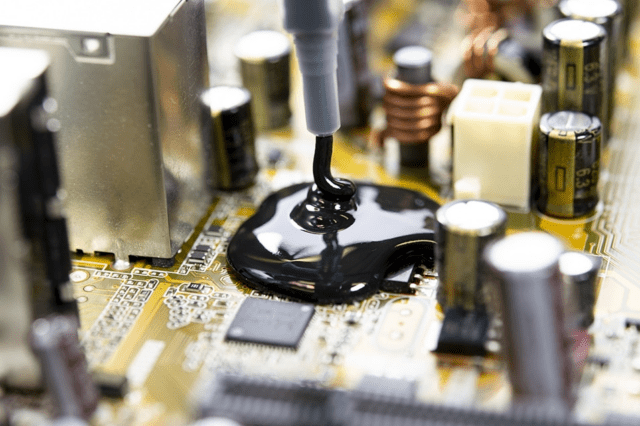
Insulation stands as the silent hero in various industries and our daily lives, playing a pivotal role in maintaining temperature stability. Insulation acts as a shield against temperature fluctuations, keeping spaces warm in winter and cool in summer, thus reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling. One of the most effective forms of insulation is thermal epoxy, which is a liquid polymer that can be sprayed or brushed onto surfaces and then hardens to create a layer of thermal conductive. This type of insulation is especially beneficial for industrial and commercial settings. To learn more about thermal epoxy and its benefits, visit https://housebouse.com/.

A. Introduction To Thermal Epoxy Resins As A Powerful Insulation Material
In the realm of insulation materials, thermal epoxy resins emerge as a formidable contender, offering a unique blend of versatility, durability, and efficiency. Unlike traditional insulation options, such as fiberglass or foam, thermal epoxy resins provide a high level of thermal conductivity while boasting exceptional mechanical strength. This makes them particularly well-suited for applications where both insulation and structural integrity are paramount.
Thermal epoxy resins consist of a matrix of epoxy resin infused with thermally conductive fillers, such as ceramics or metallic particles. This combination not only enhances thermal insulation properties but also endows the material with remarkable electrical insulation capabilities, making it indispensable in electrical and electronic applications.
With these introductory insights, let’s delve deeper into the realm of insulation to understand its significance and the diverse array of materials at its disposal.
II. Introduction To Thermal Epoxy Resins
A. Definition And Composition Of Epoxy Resins
Epoxy resins are a type of thermosetting polymer renowned for their exceptional strength, durability, and versatility. Composed of epoxide functional groups, these resins undergo a chemical reaction known as curing when combined with a hardening agent, typically amines or acids. This curing process forms a cross-linked network, transforming the liquid resin into a solid, rigid material with remarkable thermal and mechanical properties.
B. Properties That Make Epoxy Resins Suitable For Insulation Purposes
Epoxy resins possess several key properties that render them highly effective as insulation materials. Their low thermal conductivity ensures minimal heat transfer, making them ideal for applications where temperature stability is paramount. Additionally, epoxy resins exhibit excellent adhesion to various substrates, allowing for seamless integration into diverse systems. This adhesive quality not only enhances insulation performance but also contributes to the material’s longevity and reliability.
Moreover, epoxy resins boast exceptional chemical and moisture resistance, ensuring long-term insulation effectiveness even in harsh environments. Their resistance to degradation from chemicals, moisture, and UV radiation further enhances their suitability for a wide range of insulation applications.
C. Applications Of Epoxy Resins In Insulation
The versatility of epoxy resins lends itself to a myriad of insulation applications across industries. In the construction sector, epoxy resins are utilized for insulating building envelopes, roofs, and walls, improving energy efficiency and reducing heating and cooling costs. Their ability to adhere to various substrates makes them particularly well-suited for sealing gaps and cracks, enhancing overall insulation performance.
In electrical and electronic applications, epoxy resins serve as encapsulants and potting compounds, providing electrical insulation and protection against environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and vibrations. From circuit boards and transformers to sensors and power cables, epoxy resins play a crucial role in safeguarding delicate electronic components from damage and ensuring reliable performance.
Furthermore, epoxy resins find applications in the aerospace, automotive, and marine industries, where lightweight, high-strength insulation solutions are essential for enhancing fuel efficiency, reducing emissions, and ensuring operational safety.
III. The Science Behind Thermal Conductive With Epoxy Resins
A. Molecular Structure And Thermal Conductivity Of Epoxy Resins
The molecular structure of epoxy resins plays a pivotal role in their thermal insulation properties. The cross-linked network formed during the curing process creates a rigid, three-dimensional structure with limited mobility of molecules. This structure impedes the transfer of heat energy through the material, resulting in low thermal conductivity. As a result, epoxy resins effectively trap heat within a system, maintaining temperature stability and enhancing insulation efficiency.
B. Mechanisms Of Heat Transfer And How Epoxy Resins Disrupt Them
Epoxy resins disrupt these mechanisms through their unique properties and structure. Conduction, the transfer of heat through direct contact between molecules, is hindered by the rigid cross-linked network of epoxy resins, which limits the movement of heat-carrying particles. Convection, the transfer of heat through fluid motion, is minimized due to the material’s low porosity and viscosity, reducing the circulation of heat-carrying fluids within the insulation system. Additionally, epoxy resins exhibit low emissivity, meaning they absorb and emit minimal thermal radiation, further enhancing their insulation effectiveness.
IV. Applications Of Thermal Epoxy Resins
A. Electronics Industry: Insulating Electronic Components
In the fast-paced world of electronics, thermal management is critical for ensuring the reliability and performance of electronic devices. Thermal epoxy resins play a vital role in insulating and protecting delicate electronic components from heat-related damage and environmental stressors. These resins are commonly used as encapsulants and potting compounds, providing electrical insulation and mechanical support to components such as integrated circuits (ICs), sensors, and connectors.
By encapsulating electronic components in thermal epoxy resins, manufacturers can shield them from moisture, dust, and mechanical shock, thus extending their operational lifespan and reliability. Additionally, the high thermal conductivity of epoxy resins helps dissipate heat generated during device operation, preventing overheating and maintaining optimal performance. From consumer electronics to industrial automation systems, thermal epoxy resins are indispensable for ensuring the longevity and reliability of electronic devices in various applications.
B. Aerospace Industry: Thermal Insulation In Spacecraft And Aircraft
In the aerospace industry, where extreme temperatures and harsh environments are commonplace, thermal insulation plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and functionality of spacecraft and aircraft. Thermal epoxy resins are utilized as insulation materials in a wide range of aerospace applications, including thermal protection systems, cryogenic storage tanks, and electronic enclosures.
In spacecraft, thermal epoxy resins are employed to insulate critical components from the intense heat of re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere or the frigid temperatures of deep space. These resins provide a lightweight and durable solution for thermal management, ensuring the structural integrity and performance of spacecraft during their missions.
Similarly, in aircraft, thermal epoxy resins are used to insulate fuel tanks, engine components, and avionics systems from temperature extremes and environmental hazards. By incorporating thermal epoxy resins into aircraft design, manufacturers can enhance fuel efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and improve overall safety and reliability.
V. Conclusion
Insulation stands as a cornerstone of modern engineering, enabling energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, and enhanced comfort across various industries and applications. Thermal epoxy resins, with their exceptional thermal conductive properties and versatility, play a crucial role in advancing insulation technology and addressing the evolving needs of industry and society. From providing reliable insulation for buildings and homes to protecting sensitive electronics and equipment, thermal epoxy resins offer a wide range of benefits and applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are thermal epoxy resins, and how do they differ from traditional insulation materials?
Thermal epoxy resins are polymer-based materials known for their exceptional thermal insulation properties. Unlike traditional materials like fiberglass or foam, epoxy resins offer higher thermal resistance and can be more precisely tailored to specific applications.
Q: How do thermal epoxy resins work to provide insulation?
Thermal epoxy resins work by forming a barrier that inhibits the transfer of heat energy. Their molecular structure and composition disrupt the flow of thermal energy, effectively insulating the enclosed space or surface.
Q: What are the primary advantages of using thermal epoxy resins for insulation?
Thermal epoxy resins offer several advantages, including high thermal resistance, low thermal conductivity, chemical and moisture resistance, durability, and versatility in application across various industries.
Q: What industries commonly utilize thermal epoxy resins for insulation?
Thermal epoxy resins find widespread use in industries such as electronics, aerospace, automotive, construction, and renewable energy. They are employed for insulating electronic components, spacecraft and aircraft, buildings, and infrastructure.
Q: Can thermal epoxy resins withstand extreme temperatures and harsh environments?
Yes, thermal epoxy resins are engineered to withstand a wide range of temperatures and environmental conditions. They exhibit excellent stability and performance even in extreme heat or cold, as well as in corrosive or high-pressure environments.










